CASE STUDY: NORTHERN GREECE SEWER SYSTEM
| Case Study | Sewer System |
| Location | Northern Greece |
| Target | Odour Control |
| Populations Equivalent | 12 000 |
| Flowrate | 2500 m3/day |
| Treated wastewater | Municipal |
| Parameter | Suspended Solids | COD | TN | TP |
| Units | mg/l | mg/l | mg/l | mg/l |
| Input (average) | 250 | 400 | 55 | 12 |
| Sludge Production Before Application (average) | 20-25 (tn/day) | |||
| Sludge Production After Application (average) | 0 (tn/day) | |||
| Reduction | 100% |
|---|
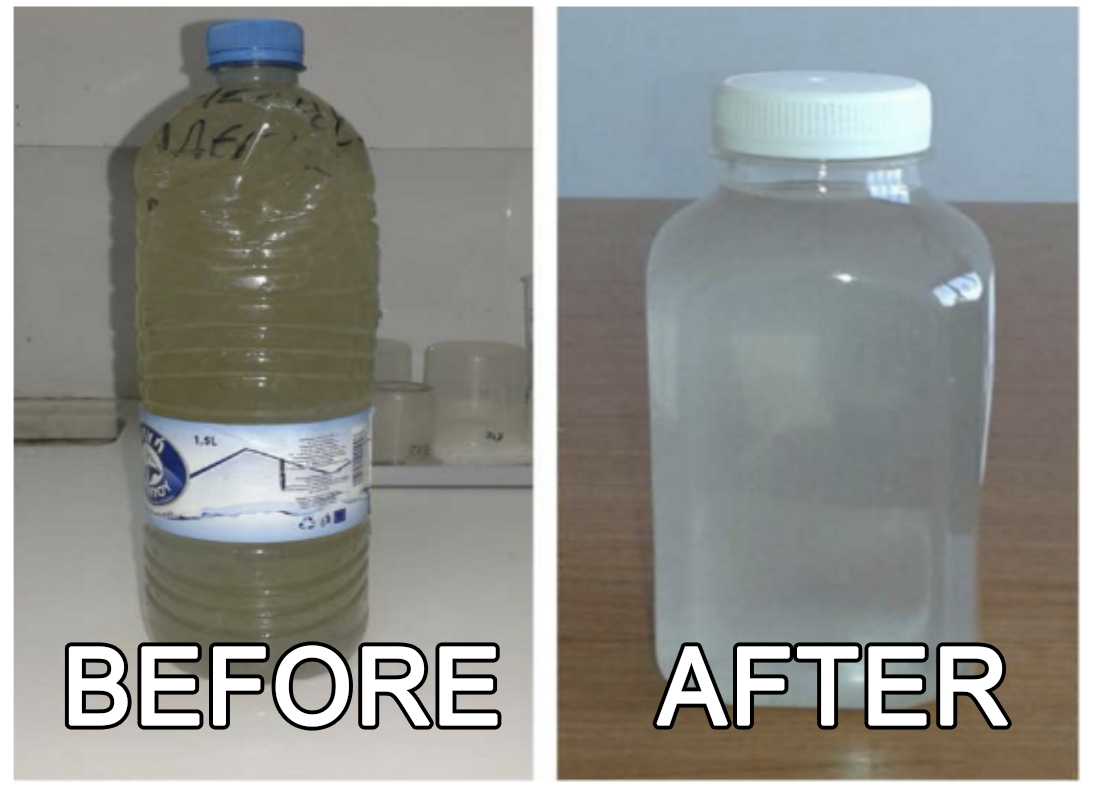

REMARKS
- The wastewater parameters entering the WWTP were significantly reduced resulting in the overall reduction of incoming loading.
- Odors, fats, oils and grease in the sewer grid, manholes and pumping stations were eliminated.
- Sewer pipelines and pumping stations were cleaned and therefore the standard cleaning maintenance was not required
CASE STUDY: LAKE REHABILITATION
| Case Study | LAKE REHABILITATION |
| Location | Northern Greece |
| Target | Water Quality Improvement & Odour Control |
| Populations Equivalent | 280 000 m3 |
| Flowrate | < 30 m3 /hr |
| Treated wastewater | Surface &Treated sewage water |
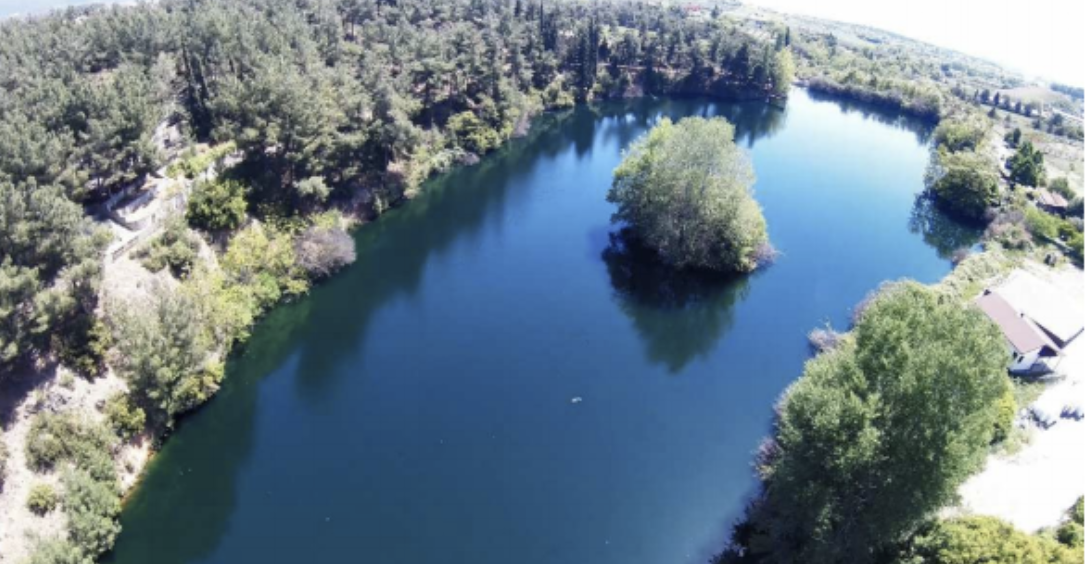

REMARKS
- Two lakes were treated
- Lake No1 approximate volume 30 000 m3 and Lake No2 of 250 000 m3
- The inflow id surface water and effluent from a wastewater treatment plant
- The implementation target is rehabilitation of the two lakes
- Combination of Facultative Microorganisms were used over three months
- An increased dosage was used during the cultivation period (first month of application)
- Total microbial product quantity used was approximately 110 kg
- All monitored parameters (Turbidity, TN, TP etc.) were improved and the rehabilitation was achieved
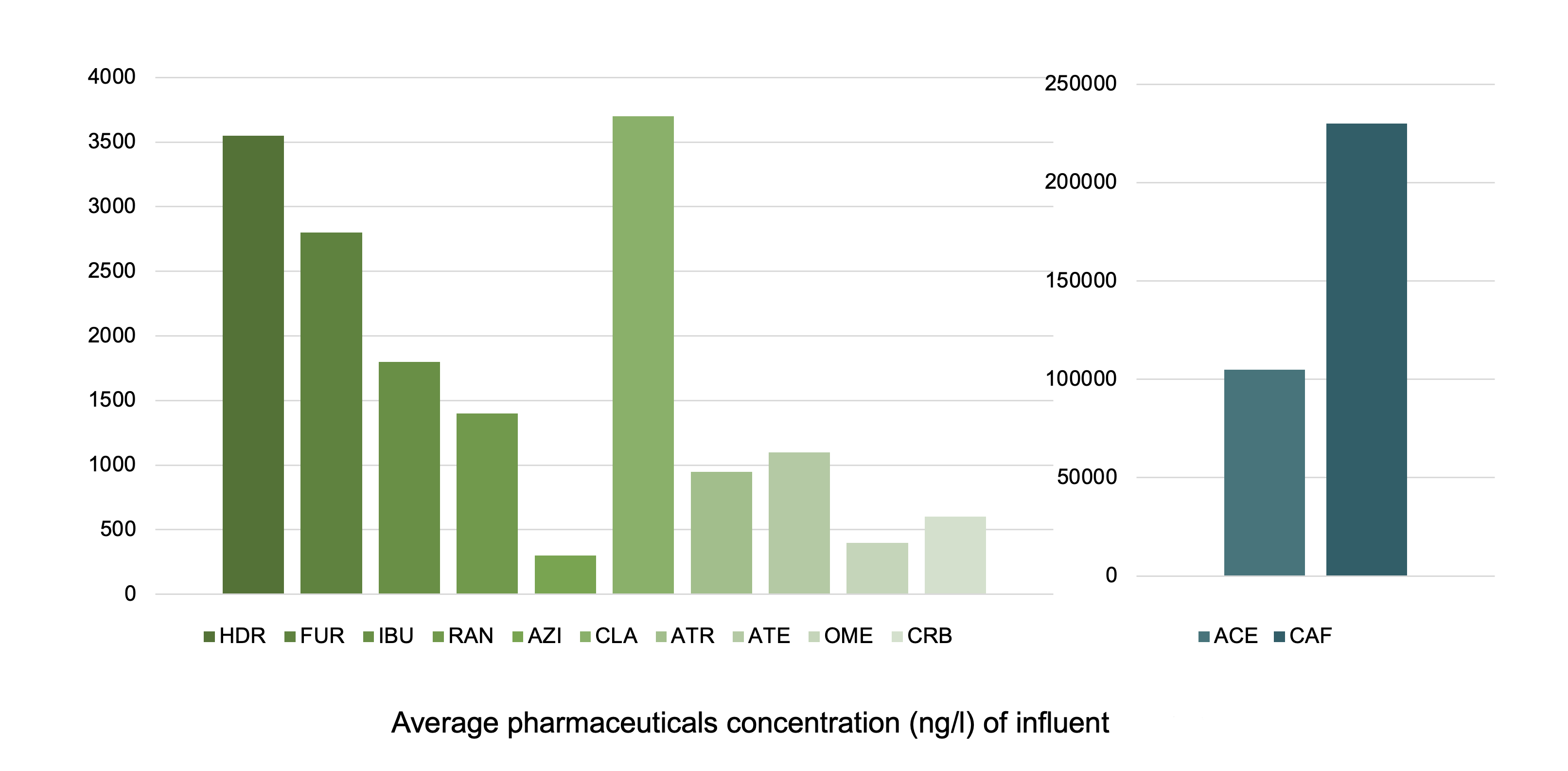
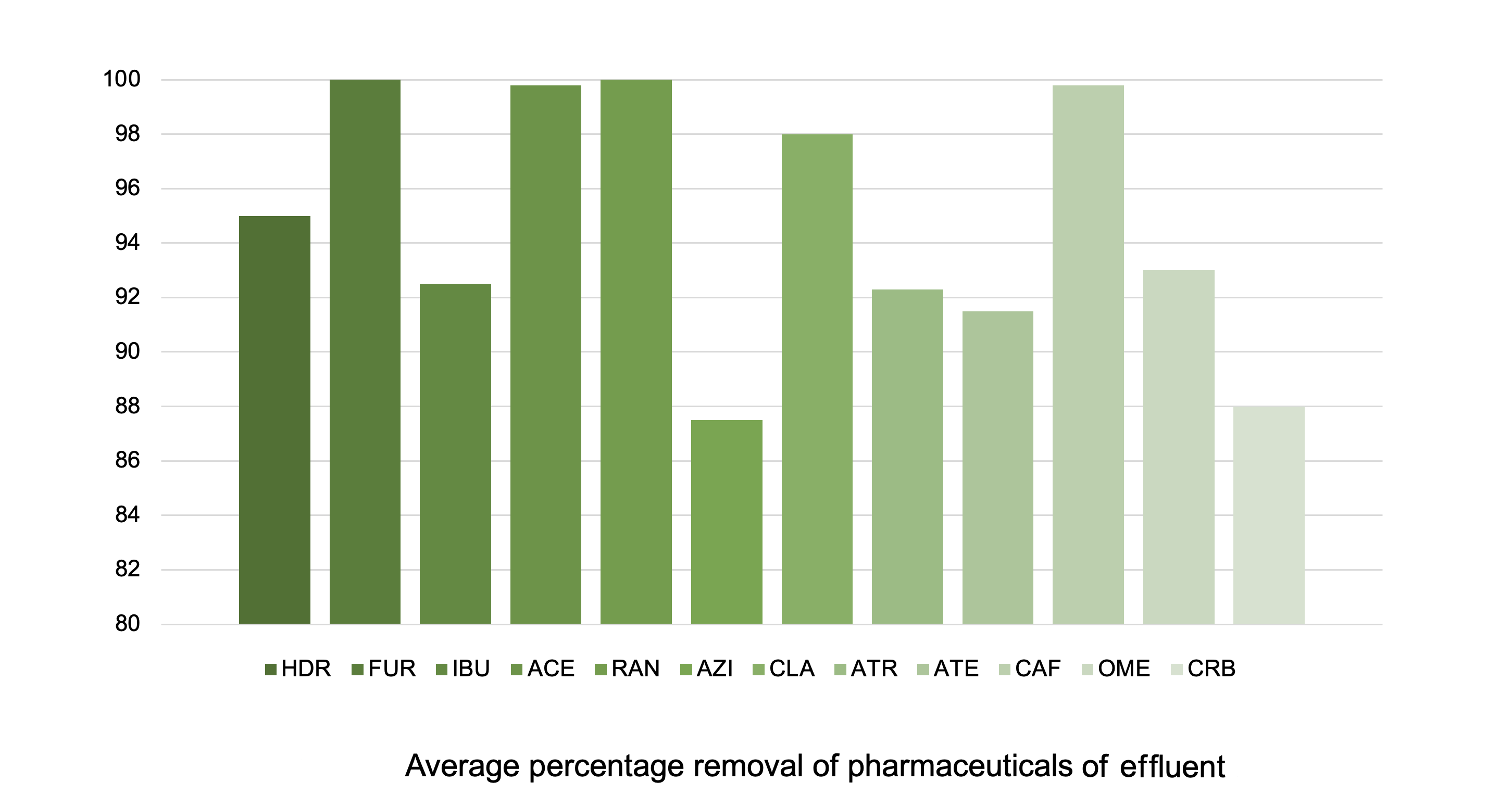
MICROPOLLUTANTS IN WASTEWATER
The occurrence of micropollutants in various streams of municipal wastewater treatment plants creates serious environmental issues. The increased use of pharmaceuticals, caffeine etc. gradually increases the concentration of the micropollutants in the wastewater treatment plants and finally in the recipient water bodies. The Ydro Process® degrades micropollutants at a very high efficiency saving enormous investments required to produce a similar result. The following micropollutants were monitored:
- HDR – Hydrochlorothiazide
- FUR – Furosemide
- IBU – Ibuprofen
- RAN – Ranitidine
- AZI – Azithromycin
- CLA – Clarithromycin
- ATR – Atorvastatin
- ATE – Atenolol
- OME – Omeprazole
- CRB – Carbamazepine
- ACE – Acetaminophen
- CAF – Caffeine